"A plurality of patent filings from
a plurality of highly capable engineers, each with a unary idea to make
a described method or apparatus smaller, faster, cheaper or better, are
iteratively presented in a time linear and serial manner." -- Rick Melick :)
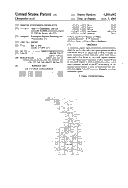
This is a (partial?) listing of the patents owned by Commodore at one point or another. If it is not the entire portfolio, then its a good representative sample at least. Please let me know if you are aware of any that are missing!
Of the forty-seven patents filed, six are design patents (most by Ira Velinsky). One that stood out to me describes a musical tone generator for use in greeting cards, such as the Hallmark musical cards we can now buy today! I think David Haynie wins for longest title, and Henri Rubin wins for most use of the phrase, "computer system."
The distribution of patent filings per calendar year looks like the histogram below. Patent filings are not cheap, so it isn't surprising to see a the bulk of them in the mid-to-late 1980s, when Commodore was rolling in dough.
Ironically, it was a patent infringement claim against Commodore by CadTrack concerning the CD32 which reportedly bankrupt the company in the end. (Commodore also had a patent on XOR, but different.)
1969 *
1970
1971
1972 *
1973
1974 *
1975 *
1976 ***
1977 *
1978
1979 *
1980
1981
1982 ****
1983
1984 **********
1985 *
1986 ****
1987 ******
1988 **
1989 **
1990
1991 ***
1992 **
1993 ****
Now, on with the show!
===== 1969 =====
Electric Portable Typewriter
Thomas Mcgourty
 Patent number: D220849
Filing date: Dec 10, 1969
Issue date: Jun 1, 1971
Patent number: D220849
Filing date: Dec 10, 1969
Issue date: Jun 1, 1971
The ornamental design for a typewriter, as shown and described.
===== 1972 =====
Artproof Method For Semiconductor Fabrication
P. Donald Payne
 Patent number: 3829213
Filing date: Jun 2, 1972
Issue date: Aug 1, 1974
Patent number: 3829213
Filing date: Jun 2, 1972
Issue date: Aug 1, 1974
A method of checking the adherence to design rules circuit configuration requirements and registration in artwork patterns to be used as masks in the fabrication of semiconductor devices by forming a composite multicolor display of the artwork before the masks have been made wherein each pattern except one or more is presented in a unique color and the remaining pattern is represented by the absence of a color.
===== 1974 =====
Reducing power consumption in calculators
Donald L. McLaughlin, et al.

Patent number: 3941989
Filing date: Dec 13, 1974
Issue date: Mar 2, 1976
Continuous power and a high rate clock are supplied to a calculator while it is in an execute mode and is actually decoding and processing input information, but lower duty cycle power and lower duty cycle clock pulses are supplied during the subsequent display mode, when the only requirement is to maintain and display selected information resulting from the execute cycle, so as to reduce the power consumption rate as compared to the rate during the execute mode. If there is no new execute mode within a selected time interval, the display is turned off and the duty cycle of the power and the clock supplied to the calculator are lowered still further so as to maintain (without displaying) selected stored information but to further reduce the rate of power consumption.
===== 1975 =====
Integrated circuit microprocessor with parallel binary adder having on-the fly correction to provide decimal results
Charles Ingerham Peddle, et al.

Patent number: 3991307
Filing date: Sep 16, 1975
Issue date: Nov 9, 1976
Disclosed is an integrated circuit microprocessor with a parallel binary adder whose output can be corrected on-the-fly to provide decimal results. The correction is by logical gating which operates selectively and on-the-fly, that is, while the sum from the output of the binary adder is being transferred to an accumulator. As a result, the same binary adder can provide the binary sum of the operands supplied to it, or the binary coded decimal sum of bcd operands, or the binary coded decimal difference of bcd operands, in a single operating cycle and without the need to recycle the sum of the operands through the adder. This single cycle correction significantly speeds up the operation of the invented microprocessor as compared to known prior art microprocessors which recycle the adder output when a binary coded decimal sum or difference is required.
===== 1976 =====
Interval timer arrangement in a microprocessor system
William D. Mensch, Jr.
 Patent number: 4099232
Filing date: Sep 14, 1976
Issue date: Jul 4, 1978
Patent number: 4099232
Filing date: Sep 14, 1976
Issue date: Jul 4, 1978
An interval timer in a MOS IC microprocessor system uses a countdown register of as many stages as the data bus lines (8) but effectively doubles the capacity of that register, without increasing the number of data bus lines or repetitive loading, by interposing a prescale divide-down register between the system clock and the countdown register. The prescale register divides the system clock by one of several selectable factors equal to non-contiguous powers of two (e.g., by 1, 8, 64 or 1,024) to establish respective prescale time periods (of 1, 8, 64 or 1024 system clock pulses). One of the several possible prescaling factors is selected by a pair of lines from the system address bus. As a result, the interval timer can be configured with one load operation for an interval within a range which was possible in the prior art only with double the number of data lines and double the length of the countdown register.
Depletion mode coupling device for a memory line driving circuit
Ernie R. Hirt, et al.
 Patent number: 4081699
Filing date: Sep 14, 1976
Issue date: Mar 28, 1978
Patent number: 4081699
Filing date: Sep 14, 1976
Issue date: Mar 28, 1978
A circuit for energizing a memory drive line depending on the state of a control signal and the states of two complementary clocks uses a depletion mode MOS coupling device rather than the conventional enhancement mode device used in such cases, and energizes the memory line with a higher voltage than possible in the prior art and at better rise and fall times.
Field inversion control for N-channel device integrated circuits
John O. Paivinen, et al.
 Patent number: 4074301
Filing date: Nov 1, 1976
Issue date: Feb 14, 1978
Patent number: 4074301
Filing date: Nov 1, 1976
Issue date: Feb 14, 1978
The field inversion properties of integrated circuits incorporating N-channel MOS devices are improved by using a silicon substrate whose bulk dopant concentration is low, but whose local dopant concentration is high at the field surfaces under the field oxide separating the active surface areas where the individual N-channel MOS devices are formed. The differential doping between surface areas under the field oxide and the active surface areas of the substrate is done by non-selectively ion-implanting boron into the substrate to form a uniform low resistivity layer, removing selected portions of the low resistivity layer to expose the unimplanted, high resistivity substrate and forming the active devices at the unimplanted substrate portions. As an option, the unimplanted surface portion can be doped to an intermediate dopant concentration to improve performance.
===== 1977 =====
Stable N-channel MOS structure
John Paivinen, et al.
 Patent number: 4212100
Filing date: Sep 23, 1977
Issue date: Jul 15, 1980
Patent number: 4212100
Filing date: Sep 23, 1977
Issue date: Jul 15, 1980
An N-channel MOS integrated circuit device having a composite metal gate structure which has improved temperature stability. The gate structure uses a polysilicon layer to separate the conventional metal gate from the conventional underlying gate oxide. The metal gate and the polysilicon layer extend laterally at least to the lateral extent of the gate region. This composite metal gate structure improves the temperature stability of the IC, and may be used, for example, in read-only memory (ROM) applications. The polysilicon layer is formed without additional photolithographic steps.
===== 1979 =====
Switch scanning means for use with integrated circuits
Tom M. Hyltin
 Patent number: 4277784
Filing date: Jul 13, 1979
Issue date: Jul 7, 1981
Patent number: 4277784
Filing date: Jul 13, 1979
Issue date: Jul 7, 1981
Method and apparatus for generating a digital data word representative of the position of a switch element which is selectively engage-able with one of a plurality of driver conductors which are utilized for conducting actuating signals from a source to a data display system of the type having a plurality of display elements for visually indicating alphanumeric data. The display elements have visually perceptible and imperceptible data indicating states and are characterized by a lagging response to either the application or interruption of the actuating signal wherein a turn-on or turn-off transition interval elapses during a change from one state to the other with the preexisting state of the display element appearing to an observer to remain unchanged during the transition interval. The actuating signals are periodically applied during a load energizing interval through one or more of the driver conductors and are interrupted during a sampling interval.
===== 1982 =====
Musical tune generator
Donald Lee Black, et al.
 Publication number EP0070653 A1
Filing date: Jul 9, 1982
Publication date: Jan 26, 1983
Publication number EP0070653 A1
Filing date: Jul 9, 1982
Publication date: Jan 26, 1983
A musical tune generator has a read only memory which stores information corresponding to the notes of a preselected musical tune. An oscillator drives an address circuit which sequentially accesses the memory locations in the read only memory. A programmable frequency divider is also coupled to the oscillator output, and is controlled by a portion of the read only memory output. Output from the programmable frequency divider corresponds to notes of the preselected tune and are reproduced in an audible mode. In a preferred embodiment, the tune generator is encapsulated within a greeting card and is controlled by a switch which enables the preselected tune to be played when the greeting card is opened.
Computer
Ira Velinsky
 Patent number: D277755
Filing date: Aug 27, 1982
Issue date: Feb 26, 1985
Patent number: D277755
Filing date: Aug 27, 1982
Issue date: Feb 26, 1985
The ornamental design for a computer, as shown.
Computer
Ira Velinsky
 Patent number: D277857
Filing date: Aug 27, 1982
Issue date: Mar 5, 1985
Patent number: D277857
Filing date: Aug 27, 1982
Issue date: Mar 5, 1985
The ornamental design for a computer, as shown.
Computer
Ira Velinsky
 Patent number: D277855
Filing date: Aug 27, 1982
Issue date: Mar 5, 1985
Patent number: D277855
Filing date: Aug 27, 1982
Issue date: Mar 5, 1985
The ornamental design for a computer, as shown.
===== 1983 =====
Raster line comparator circuit for video game
David W. DiOrio
 Patent number: 4572506
Filing date: Jun 3, 1983
Issue date: Feb 25, 1986
Patent number: 4572506
Filing date: Jun 3, 1983
Issue date: Feb 25, 1986
A comparator circuit incorporated into a video game device and operated responsive to first and second non-overlapping clock pulses can be used to compare background information location to SPRITE information location for both raster line (vertical) and column (horizontal) coordinates to provide a high speed interrupt signal to a central processor unit (CPU) triggering a processing of SPRITE or other features' display instead of a processing of background display, the comparator being implemented in less silicon area and having a lower power usage than other types of circuit implementations.
Digital sine-cosine generator
Albert J. Charpentier, et al.
 Patent number: 4551682
Filing date: Jan 3, 1983
Issue date: Nov 5, 1985
Patent number: 4551682
Filing date: Jan 3, 1983
Issue date: Nov 5, 1985
A solid-state, digital logic, sine-cosine generator is provided for use in color television signal generators which contributes little or no phase shift or drift, whereby an input frequency of four times the color burst rate is used, and a first divide by two shift register operates upon that input signal frequency while a second divide by two shift register is used to obtain the proper color burst frequency as well as the 90 degree relationship for the sine and cosine signals; a series of integrators then converts the digital "square" waves to triangular and then sinusoidal signals.
Display logic circuit for multiple object priority
James W. Redfield, et al.
 Patent number: 4561659
Filing date: Jan 6, 1983
Issue date: Dec 31, 1985
Patent number: 4561659
Filing date: Jan 6, 1983
Issue date: Dec 31, 1985
A display control circuit provides the logical determination of display information for each dot point of a color television or other display device used in connection with an electronic game for displaying up to eight "targets", as well as background information, according to a preassigned software defined priority whereby hardware circuitry encodes background-to-target software information and then decodes all game display circuit information to generate a color display code to the color television-type display device, this hardware utilizing a reduced space on a large scale integrated (LSI) circuit.
Clocked self booting logical "EXCLUSIVE OR" circuit
James W. Redfield
 Patent number: 4562365
Filing date: Jan 6, 1983
Issue date: Dec 31, 1985
Patent number: 4562365
Filing date: Jan 6, 1983
Issue date: Dec 31, 1985
A solid state logical "EXCLUSIVE OR" circuit for implementation in NMOS circuitry utilizes existing non-overlapping clock pulses for self-booting circuit conditioning, enabling ultra-fast propagation times and minimal power drain during circuit operation, whereof row driver circuit design concepts are utilized and silicon area is minimized and two, non-overlapping, low impedance pulses, normally present in the circuit environment are utilized.
Self booting logical or circuit
James W. Redfield
 Patent number: 4599528
Filing date: Jan 17, 1983
Issue date: Jul 8, 1986
Patent number: 4599528
Filing date: Jan 17, 1983
Issue date: Jul 8, 1986
A solid state logical "OR" circuit for implementation with NMOS circuitry has self-booting clock pulse conditioning for ultra fast propagation times and minimal power dissipation, whereof memory row driver concepts are utilized and silicon area is minimized.
Self booting logical AND circuit
James W. Redfield
 Patent number: 4570085
Filing date: Jan 17, 1983
Issue date: Feb 11, 1986
Patent number: 4570085
Filing date: Jan 17, 1983
Issue date: Feb 11, 1986
A solid state logical "AND" circuit implementation in NMOS circuitry has clock pulse conditioning providing self booting voltage levels for ultra fast propagation times and minimal power dissipation, where memory row driver concepts are utilized and silicon area is minimized, and two, low impedance, non-overlapping clock pulses, normally present in the environment are utilized.
Sound interface circuit
Robert J. Yannes
 Patent number: 4677890
Filing date: Feb 27, 1983
Issue date: Jul 7, 1987
Patent number: 4677890
Filing date: Feb 27, 1983
Issue date: Jul 7, 1987
A sound interface circuit is implemented in large scale integrated circuitry (LSI) on a single chip to provide 3 voice electronic music synthesizer/sound effects, and is compatible with instructions from commercially available microprocessors; whereof a wide range, high-resolution control of pitch (frequency) tone color (harmonic content) and dynamics (volume) is achieved and specialized control circuitry minimizes software overhead, facilitating use in arcade/home video games and low cost musical instruments.
Printer
Ira L. Velinsky
 Patent number: D281503
Filing date: Apr 4, 1983
Issue date: Nov 26, 1985
Patent number: D281503
Filing date: Apr 4, 1983
Issue date: Nov 26, 1985
The ornamental design for a printer, as shown and described.
Video game cartridge case
Ira L. Velinsky
 Patent number: D280322
Filing date: Apr 4, 1983
Issue date: Aug 27, 1985
Patent number: D280322
Filing date: Apr 4, 1983
Issue date: Aug 27, 1985
The ornamental design for a video game cartridge case, as shown.
Video sound and system control circuit
David W. DiOrio, et al.
 Patent number: 4569019
Filing date: Jun 3, 1983
Issue date: Feb 4, 1986
Patent number: 4569019
Filing date: Jun 3, 1983
Issue date: Feb 4, 1986
Programmable I/O (input/output) interface circuitry provides video and audio signals, needed for a video computer/game, to a commercial color television type display/monitor and may be implemented in HMOS, (H type metal oxide semiconductor) large-scale-integrated circuitry. The system architecture allows for reduced chip count, and improved reliability while providing adequate synchronization pulses, luminance level signals, chrominance phase shift signals, raster control and cursor control video and three independently controlled audio voices. A software selectable keyboard latch input, plural speed processing for faster operation when outside the active display area or during blanking, all system control signals necessary for system operation and 3 independently controlled interrupt generating timers.
===== 1985 =====
Video game and personal computer
Jay G. Miner, et al.
 Patent number: 4777621
Filing date: Jul 19, 1985
Issue date: Oct 11, 1988
Patent number: 4777621
Filing date: Jul 19, 1985
Issue date: Oct 11, 1988
A video game home computer is implemented in NMOS (n type metal oxide semiconductor) technology with plural microprocessors. Centralized bus architecture and direct memory access (DMA) techniques are employed. A video display generator provides color signal outputs to drive a commercial television receiver display. This display generator receives inputs from both microprocessors and obtains data directly from memory. A bit map of display information is kept in memory, wherein bits of information in memory image the precise screen display for each instance in time. A bit map manipulator circuit performs, under microprocessor direction, logic function manipulation of the bit map data. Access between system components is accomplished via the bus architecture on a priority queue basis. Chip count and chip area is minimized.
===== 1986 =====
Memory management unit for addressing an expanded memory in groups of non-contiguous blocks from the entire memory configuration
David W. Di Orio
 Patent number: 4761736
Filing date: Jan 2, 1986
Issue date: Aug 2, 1988
Patent number: 4761736
Filing date: Jan 2, 1986
Issue date: Aug 2, 1988
A n-channel memory management circuit operates as an interface unit between a microprocessor, which microprocessor is normally capable of addressing only 64K bytes of memory, to provide expandable memory configurations with a memory capacity of at least 128K bytes of read only memory (ROM) and 128K bytes of random access memory (RAM) which are directly accessed by the microprocessor in 64K bytes blocks or "windows" consisting of smaller size non-contiguous blocks from the entire memory configuration.
Personal computer apparatus for block transfer of bit-mapped image data
Jay G. Miner, et al.
 Patent number: 4874164
Filing date: Jul 18, 1986
Issue date: Oct 17, 1989
Patent number: 4874164
Filing date: Jul 18, 1986
Issue date: Oct 17, 1989
A computer that provides data to a video display using a bitmap display memory organization and bitplane addressing. Separate control is provided for two bitplane backgrounds and for eight reusable and easily movable sprites. Additional logic allows for dynamically-controllable inter-object priority and collision detection among data in each of the bitplane backgrounds and sprites. A coprocessor provides for video beam-synchronized changes to data in registers, freeing the main processor for general purpose computing tasks. A block image transfer is provided to rapidly copy data in large blocks from one memory location to another. In hold-and-modify mode, color output circuitry holds the value for a previously displayed pixel while bitplane data modifies those values, allowing for simultaneous display of a greatly increased number of colors.
Current mirror amplifier
Jonathan S. Radovsky
 Patent number: 4686487
Filing date: Jul 28, 1986
Issue date: Aug 11, 1987
Patent number: 4686487
Filing date: Jul 28, 1986
Issue date: Aug 11, 1987
A current mirror amplifier is provided wherein the feedback path around a diode-connected device is modified by adding a resistor in series with the input terminal of the diode-connected device in order to cancel a pole which appears at the unity-gain frequency. This will improve the frequency response and provide for increased bandwidth. The added resistor may be realized in MOS technology by employing a tracking MOS device.
Raster monitor for video game displays
Albert J. Charpentier
 Patent number: 4813671
Filing date: Sep 22, 1986
Issue date: Mar 21, 1989
Patent number: 4813671
Filing date: Sep 22, 1986
Issue date: Mar 21, 1989
A monitoring circuit incorporated into a video game display device is operated responsively to first and second non-overlapping clock pulses and monitors raster line status in comparison to a stored raster address and provides a high speed raster scan interrupt when that address is achieved, triggering a SPRITE or other feature(s) display.
===== 1987 =====
Circuit for interfacing mouse input device to computer system
Hedley Davis, et al.
 Patent number: 4886941
Filing date: May 19, 1987
Issue date: Dec 12, 1989
Patent number: 4886941
Filing date: May 19, 1987
Issue date: Dec 12, 1989
A computer system mouse-type input device. Movements of a track-ball motion sensor are converted to quadrature signals and are accumulated in a counting circuit. The contents of the counter are pulse-position modulated with waveforms characteristic of a resistive-capacitive charging circuit and are read periodically by a computer input channel normally used for input of potentiometer-generated commands. The pulse-position modulated signals are converted to digital values used to position the cursor on a display screen.
Computer video demultiplexer
Hedley C. Davis
 Patent number: 4851826
Filing date: May 29, 1987
Issue date: Jul 25, 1989
Patent number: 4851826
Filing date: May 29, 1987
Issue date: Jul 25, 1989
A computer video demultiplexer for combining a plurality of low resolution, video input signals into a plurality of higher horizontal and vertical resolution video output signals. Control signals for the video demultiplexer are coded on non-displayed video scan lines which are uniquely addressable so that several demultiplexers operated from one video signal may control a number of high resolution peripheral devices.
Peripheral control circuitry for personal computer
Glenn Keller, et al.
 Publication number EP0317567 A4
Filing date: Jul 14, 1987
Publication date: Mar 13, 1991
Publication number EP0317567 A4
Filing date: Jul 14, 1987
Publication date: Mar 13, 1991
Control and interface circuitry for right and left audio channels, a disk storage medium, a UART and up to four potentiometer ports. The design includes a separate interrupt priority control and status circuit for channel control communication with the personal computer microprocessor. Much of the burden associated with personal computer microprocessor peripheral control is alleviated by employing a separate address and data bus and direct memory access for some peripheral control circuits. In operation, each control circuit includes a data register for the reception and transmission of data via the data bus; a register address decoder decodes device addresses appearing on the address bus, enabling, via separate enabling lines, the corresponding devices for the reception of data. Audio and disk channel control logic access memory directly by sending requests to a DMA request logic parallel - to - serial multiplexor.
Cursor controlled user interface system
J. Robert Mical
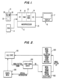 Publication number EP0316325 B1
Filing date: Jul 14, 1987
Publication date: Feb 1, 1995
Publication number EP0316325 B1
Filing date: Jul 14, 1987
Publication date: Feb 1, 1995
Menu item selection is performed in a personal computer system through use of a mouse device which has means to allow the user to call up onto the display a header block which performs the function of the menu bar and to erase the header block from the screen when menu operations are not required. Multiple menu items can be selected during the same menu session by using a pair of mouse buttons and to generate a sequence of selection commands which are utilized by unique system software to accumulate plural item selections without terminating the menu operation.
Data input circuit with digital phase locked loop
Glenn Keller
 Publication number EP0316340 B1
Filing date: Jul 14, 1987
Publication date: Jan 12, 1994
Publication number EP0316340 B1
Filing date: Jul 14, 1987
Publication date: Jan 12, 1994
A data input circuit processes data pulses received from a disk drive and adjusts itself to compensate for phase errors and for frequency errors while the data is being read. The data input circuit keeps track of the times of arrival of prior data pulses in order to measure and correct for frequency and phase drift of the data pulses being read from the disk. An up-down counter, mux, and an adder are included in the phase locked loop to digitally indicate the precise time of arrival of the data pulses from the disk. Decoder circuits process the digital arrival time information for a data pulse or pulses and generate correction signals that are fed back to the counter and adder circuits. The correction signals adjust the duration and start/stop time of each inspection window by causing the duration and/or start/stop time for one complete cycle of the adder to vary. After each complete adder cycle, a carry signal is sent to a buffer. If a data pulse was received at any time during that one adder cycle (which corresponds to an inspection window), a ''1'' will be input and stored. Thus, the buffer will temporarily store data bits that match the data contained in the disk drive being transmitted to the input circuit.
Display generator circuitry for personal computer system.
Dave Dean, et al.
 Publication number EP0318517 A1
Filing date: Jul 14, 1987
Publication date: Jun 7, 1989
Publication number EP0318517 A1
Filing date: Jul 14, 1987
Publication date: Jun 7, 1989
A video game including an auxiliary processing circuit that enhances display capabilities. The circuit comprises a bi-directional buffer, a circuit data bus, an address bus, a unidirectional buffer, two multiplexers, and a bit map image manipulation circuit.
===== 1988 =====
Fast gate and adder for microprocessor ALU
William F. Gardei
 Patent number: 4989174
Filing date: Oct 27, 1988
Issue date: Jan 29, 1991
Patent number: 4989174
Filing date: Oct 27, 1988
Issue date: Jan 29, 1991
A fast logic gate wherein the gate output assumes a first binary state when two or more of the gate inputs assume the same predetermined binary states and wherein the gate output assumes a second binary state otherwise. The delay in propagating the gate output based on a transition at a predetermined one of the gate inputs is relatively small. In a preferred application, the gate is utilized in a microprocessor ALU, more particularly, the portion of each adder bit which generates the carry output, and the predetermined gate input is the carry input of the adder bit. The microprocessor can therefore execute instructions which involve addition or subtraction operations, such as relatively addressing instructions, much more quickly.
System for accelerating execution of program instructions by a microprocessor
William F. Gardei, et al.
 Patent number: 5088035
Filing date: Dec 9, 1988
Issue date: Feb 11, 1992
Patent number: 5088035
Filing date: Dec 9, 1988
Issue date: Feb 11, 1992
A latch transfers fetched op-code to PLA for execution at the earliest opportunity following execution of a prior single cycle op-code.
===== 1989 =====
Universal connector device for bus networks in host computer/co-processor computer system
Henri Rubin
 Patent number: 4954949
Filing date: Oct 2, 1989
Issue date: Sep 4, 1990
Patent number: 4954949
Filing date: Oct 2, 1989
Issue date: Sep 4, 1990
A connector device for use in communication of data between the central processing unit (CPU) bus of a host computer system and the CPU bus of a co-processor computer system, between the CPU bus of the host computer system and an expansion card used with the host computer system, and between the CPU bus of the co-processor computer system and an expansion card used with the co-processor computer system using a bridge card includes a plurality of host computer system expansion slots and a plurality of co-processor computer system expansion slots configured so that at least one host computer system expansion slot and at least one co-processor computer system expansion slot form an in-line pair to accept the bridge card.
Beam synchronized coprocessor
Jay G. Miner, et al.
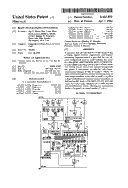 Patent number: 5103499
Filing date: Oct 16, 1989
Issue date: Apr 7, 1992
A computer that provides data to a video display using a bitmap display memory organization and bitplane addressing. Separate control is provided for two bitplane backgrounds and for eight reusable and easily movable sprites. Additional logic allows for dynamically-controllable inter-object priority and collision detection among data in each of the bitplane backgrounds and sprites. A coprocessor provides for video beam-synchronized changes to data in registers, freeing the main processor for general purpose computing tasks. A block image transfer-er is provided to rapidly copy data in large blocks from one memory location to another. In hold-and-modify mode, color output circuitry holds the values for a previously displayed pixel while bitplane data modifies those values, allowing for simultaneous display of a greatly increased number of colors.
Patent number: 5103499
Filing date: Oct 16, 1989
Issue date: Apr 7, 1992
A computer that provides data to a video display using a bitmap display memory organization and bitplane addressing. Separate control is provided for two bitplane backgrounds and for eight reusable and easily movable sprites. Additional logic allows for dynamically-controllable inter-object priority and collision detection among data in each of the bitplane backgrounds and sprites. A coprocessor provides for video beam-synchronized changes to data in registers, freeing the main processor for general purpose computing tasks. A block image transfer-er is provided to rapidly copy data in large blocks from one memory location to another. In hold-and-modify mode, color output circuitry holds the values for a previously displayed pixel while bitplane data modifies those values, allowing for simultaneous display of a greatly increased number of colors.
===== 1991 =====
Apparatus and method for transferring interleaved data objects in mass storage devices
Carl E. Sassenrath
 Patent number: 5293606
Filing date: Apr 2, 1991
Issue date: Mar 8, 1994
Patent number: 5293606
Filing date: Apr 2, 1991
Issue date: Mar 8, 1994
A system for transferring interleaved data objects in mass storage devices into separate destinations in a system memory is described. The method includes the steps of determining for each of the data objects a destination address and a size; one time seeking of a data object from a location of the mass storage means; transferring data from the data object into the destination address, wherein the data has a size equal to the size for the data object; and repeating the transferring step for subsequent data objects.
System for relocating a multimedia presentation on a different platform by extracting a resource map in order to remap and relocate resources
John D. Gerlach, Jr., et al.
 Patent number: 5317732
Filing date: Apr 26, 1991
Issue date: May 31, 1994
Patent number: 5317732
Filing date: Apr 26, 1991
Issue date: May 31, 1994
A process performed in a data processing system includes receiving an input selecting one of the plurality of multimedia presentations to be relocated from the first memory to the second memory, scanning the linked data structures of the selected multimedia presentation to recognize a plurality of resources corresponding to the selected multimedia presentation, and generating a list of names and locations within the selected multimedia presentation corresponding to the identified plurality of resources. The process also includes renaming the names on the generated list, changing the names of the identified plurality of resources in the selected multimedia presentation to the new names on the generated list, and moving the selected multimedia presentation and the resources identified on the generated list to the second memory.
Bus arbitration system for granting bus access to devices following two-wire bus arbitration protocol and devices following three-wire bus arbitration protocol
David B. Haynie
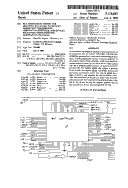 Patent number: 5276887
Filing date: Jun 6, 1991
Issue date: Jan 4, 1994
Patent number: 5276887
Filing date: Jun 6, 1991
Issue date: Jan 4, 1994
A bus arbitration system is capable of granting access to an expansion bus to devices following two-wire bus arbitration protocol or a three-wire bus arbitration protocol. The bus arbitration system receives a plurality of bus request signals from a plurality of devices. Each bus request signal is made up of one or more coded pulses and has a predetermined priority. A priority encoder receives the bus request signal and assigns a priority level to each bus request signal. An arbiter determines and stores in memory which bus request signal has a highest priority and whether the device follows two-wire bus arbitration protocol or a three-wire bus arbitration protocol. The expansion bus grants access to the bus to the device having the highest priority once a previous device if any, has relinquished the bus.
===== 1992 =====
Binary to unary decoder for a video digital to analog converter
Robert J. Rabile
 Patent number: 5313300
Filing date: Aug 10, 1992
Issue date: May 17, 1994
Patent number: 5313300
Filing date: Aug 10, 1992
Issue date: May 17, 1994
A binary to unary decoder for a video digital to analog converter is cascade-able in both a horizontal and a vertical direction. Video data is transmitted from a video data source and received by a plurality of unary decoders which convert the video data to a corresponding number of unary digits having comparable value. The unary decoders are arranged in a number of cascaded levels. A plurality of cascaded unary block drivers receive the unary digits and transit unary output digits to a video data bus. The plurality of unary block drivers are arranged in a number of tiers having a predetermined number of individual unary block drivers. The predetermined number of cascaded unary block drivers are enabled based upon the numerical value of the video data.
Audio channel system for providing an analog signal corresponding to a sound waveform in a computer system
Glenn J. Keller, et al.
 Patent number: 5418321
Filing date: Dec 15, 1992
Issue date: May 23, 1995
Patent number: 5418321
Filing date: Dec 15, 1992
Issue date: May 23, 1995
An audio channel system provides an analog signal corresponding to a sound waveform in a computer system. The audio channel system includes a plurality of audio channels. Each audio channel contains a predetermined number of audio data samples for producing a particular sound waveform. A plurality of volume bits define a volume level of each audio data sample to be played. An audio processor processes the sound waveforms of each audio channel. The audio processor acts as a shared processing element which receives the audio data samples from each audio channel. The audio processor divides the audio data samples into a plurality of data such that the plurality of data for each audio data sample is pipelined through the audio processor in a serial manner. The plurality of data for each audio data sample for each audio channel is in various processing stages at any given time.
===== 1993 =====
Decoder for cross interleaved error correcting encoded data
Allan Havemose
 Patent number: 5412667
Filing date: Jul 8, 1993
Issue date: May 2, 1995
Patent number: 5412667
Filing date: Jul 8, 1993
Issue date: May 2, 1995
An improved method for processing a sector of data read from a CD-ROM which has been encoded using a cross-interleaved Reed Solomon (CIRS) code is time linear in the number of errors in the sector. The improved method iteratively processes the data values from the sector, which appear in each of the sets of cross-interleaved sequences, through an error detection/correction algorithm. In the first pass, a syndrome is generated for each sequence in each set. If the syndrome indicates that the sequence either contains no errors or an undetectable number of errors, the sequence is marked as being error-free. If a sequence contains a correctable error, the error is corrected and the sequence is marked as being error-free. If the syndrome indicates that the sequence contains a number of errors which may be detected but not corrected the sequence is marked as containing errors.
CD-ROM video game machine
Donald Kaminski et al
 Patent number: D356835
Filing date: Jul 23, 1993
Issue date: Mar 28, 1995
Patent number: D356835
Filing date: Jul 23, 1993
Issue date: Mar 28, 1995
The ornamental design for a CD-ROM video game machine, as shown and described.
Method and apparatus for performing multiple simultaneous error detection on data having unknown format
Edward Hepler
 Patent number: 5432801
Filing date: Jul 23, 1993
Issue date: Jul 11, 1995
Patent number: 5432801
Filing date: Jul 23, 1993
Issue date: Jul 11, 1995
An error may be detected and corrected from among a plurality of data values retrieved from a compact disk-read only memory (CD-ROM). As a stream of data values which have been retrieved from the CD-ROM are retransmitted by an appropriate DMA device, two different error detection schemes are simultaneously applied to identical copies of the retrieved data. The retrieved data is then evaluated to determine in which format data has been stored on the CD-ROM. A condition value which has been generated by the algorithm corresponding to the determined format of data on the CD-ROM is then evaluated to determine the probability of an error condition in the retrieved data. The two error detection schemes may differ solely in the location of the data values which are evaluated for errors.
Multiple linked game controllers
George Robbins
 Patent number: 5421590
Filing date: Jul 23, 1993
Issue date: Jun 6, 1995
Patent number: 5421590
Filing date: Jul 23, 1993
Issue date: Jun 6, 1995
Linked game controllers coupled to a single input port of a computer game are configured such that all controllers may be active at the same time. One controller is coupled to an input port on the computer game which has both a parallel-bit interface and a bit-serial interface. This controller provides information on its own control function via the parallel interface and information derived from each of the linked controllers via the serial interface. Each of the controllers includes a flag bit, in the provided information, that indicates whether the controller is the last controller in the sequence of linked controllers. The computer game stores data values provided by the parallel interface and then shifts values provided by the serial interface into an internal register until one of the flag bits, indicating the last controller in the sequence, has been shifted.
I have additional Commodore goodness over on my web site: http://www.geocities.ws/cbm
Are you interested in computer history? Join the irregular regulars Earl Evans, David Greelish, and Carrington Vanston, plus surprise guests, in the show where everything old is news again. Gather 'round a virtual table where today's talk is about yesterday's computers. Get the skinny from the world of vintage computer hobbyists, collectors, enthusiasts, and old school geeks. They cover modern day vintage tech events, new developments for old hardware, the revival of retro tech, the best of 8 bit culture, and take many strolls down memory lane. Head on over to http://rcrpodcast.com and explore podcasts, review show notes and be informed of upcoming episodes. You'll be glad you did!










































































